肠道微生物研究必看的经典综述
2018-01-24 小张 小张聊科研
上周我们对外泌体有关的研究进行了梳理,整理了今年新获得自助的外泌体有关的国自然基金和必看的综述(外泌体研究必看的经典综述),今天我们来看另外一个科研的热点:肠道微生物
关于肠道微生物,我们也写过一些文章:
(文章篇)S5E02:从一篇Cell看肠道菌群研究模式
(文章篇)S5E17:神经科学大牛的一篇Nature Medicine,肠道菌群与中风的免疫学原因
(文章篇)S5E05: 来篇Science提提神,从免疫角度看宿主基因-肠道微生物作用
(文章篇)S5E03:宿主通过microRNA调控肠道微生物多样性
肠道微生物研究入门必看:神奇菌群有哪些?
(策略篇)S5E1:肠道微生物,复古的科研新热点!
肠道微生物作为热点我们可以从2017年这一年发表的10以上的SCI文章上看出来:
从国自然基金来看,肠道菌群为主题的研究也确实是资助的重点,共资助285项,资助金额1.29亿。其中青年基金108项,面上项目137项,地区项目34项,重点项目有6项,其中医学部南京中医药大学战丽彬获得重点项目一项:
基于肠道菌群“从脾论治”疾病易感痰湿体质的中医治未病的生物学基础研究
下面我们就梳理下研究肠道微生物研究必看的经典综述(影响因子10+,按领域区分):
一、菌群与肿瘤
1. Anticancer effects of the microbiome and its products.
2. Microbiota: a key orchestrator of cancer therapy.
3. Cancer and the gut microbiota: an unexpected link.
1. Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease.
2. Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Pathogenesis of Obesity and Obesity-Related Metabolic Dysfunction.
3. Role of gut microbiota in atherosclerosis.
4. The gut microbiome, diet, and links to cardiometabolic and chronic disorders.
5. Bile Acid-Activated Receptors, Intestinal Microbiota, and the Treatment of Metabolic Disorders.
6. The gut microbial endocrine organ: bacterially derived signals driving cardiometabolic diseases.
7.Beyond gut feelings: how the gut microbiota regulates blood pressure.
1.Gut/brain axis and the microbiota .
2.The Central Nervous System and the Gut Microbiome.
3. Psychobiotics and the Manipulation of Bacteria-Gut-Brain Signals.
4. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease.
1. Dysbiosis and the immune system.
2. The microbiome and innate immunity.
3. The microbiota in adaptive immune homeostasis and disease.
4. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity.
5.Understanding the Holobiont: How Microbial Metabolites Affect Human Health and Shape the Immune System.
6.How nutrition and the maternal microbiota shape the neonatal immune system.
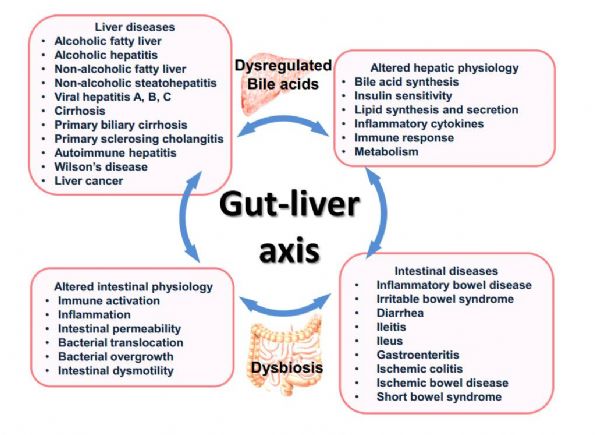
1.Gut microbiome and liver diseases.
2. Gut-liver axis in alcoholic liver disease.
3. From Hype to Hope: The Gut Microbiota in Enteric Infectious Disease.
4. Diagnostic and Prognostic Microbial Biomarkers in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.
5. Implications of microbiota and bile acid in liver injury and regeneration.
6. Changes in the Intestinal Microbiome and Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Liver Diseases: Causes or Effects?.
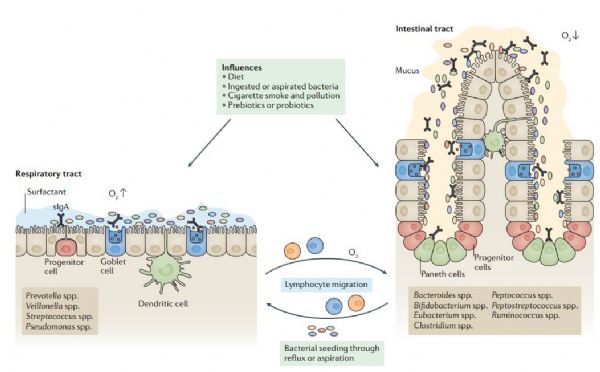
Emerging pathogenic links between microbiota and the gut-lung axis.
Microbiota in allergy and asthma and the emerging relationship with the gut microbiome.
An integrative view of microbiome-host interactions in inflammatory bowel diseases.
Microbial endocrinology: the interplay between the microbiota and the endocrine system.

本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言













#微生物#
35
谢谢分享.受益匪浅
72