B型外踝骨折,钢板放外侧还是后外侧?
2021-12-07 网络 网络
为了比较两种钢板放置位置的非计划再手术率及并发症,有学者进行了相关研究,结果发表在近期Injury杂志。
为了比较两种钢板放置位置的非计划再手术率及并发症,有学者进行了相关研究,结果发表在近期Injury杂志。


Introduction(介绍)
踝关节骨折通常采用切开复位钢板螺钉内固定治疗。非计划再手术是常见的,在许多情况下肿胀消退后,需从外踝取出突出的骨缝合螺钉。
我们假设,与将钢板置于外侧的患者相比,在外踝放置后外侧钢板的患者会有更少的再手术和并发症率。
[Introduction: Ankle fractures are commonly treated by open reduction and internal fixation with plate and screws. Unplanned return to theatre is common, in many cases to extract prominent osteosynthesis material from the lateral malleolus as swelling subsides. We hypothesised that patients operated with a posterolateral plate placement on the lateral malleolus would have fewer reoperations, and fewer complications, compared to patients with a lateral plate placement.]
Materials and Methods(病例与方法)
从我们机构前瞻性收集的所有骨科手术数据库中,我们确定了2008年1月1日至2012年4月30日期间接受钢板固定的664例踝关节骨折。分析X光片仅纳入AO/OTA 44-B骨折(n = 453),并根据钢板定位确定研究组。评估医院档案,以确定可能的混杂因素,以及任何计划外的再次手术或并发症。并发症根据Dindo-Clavien分级。
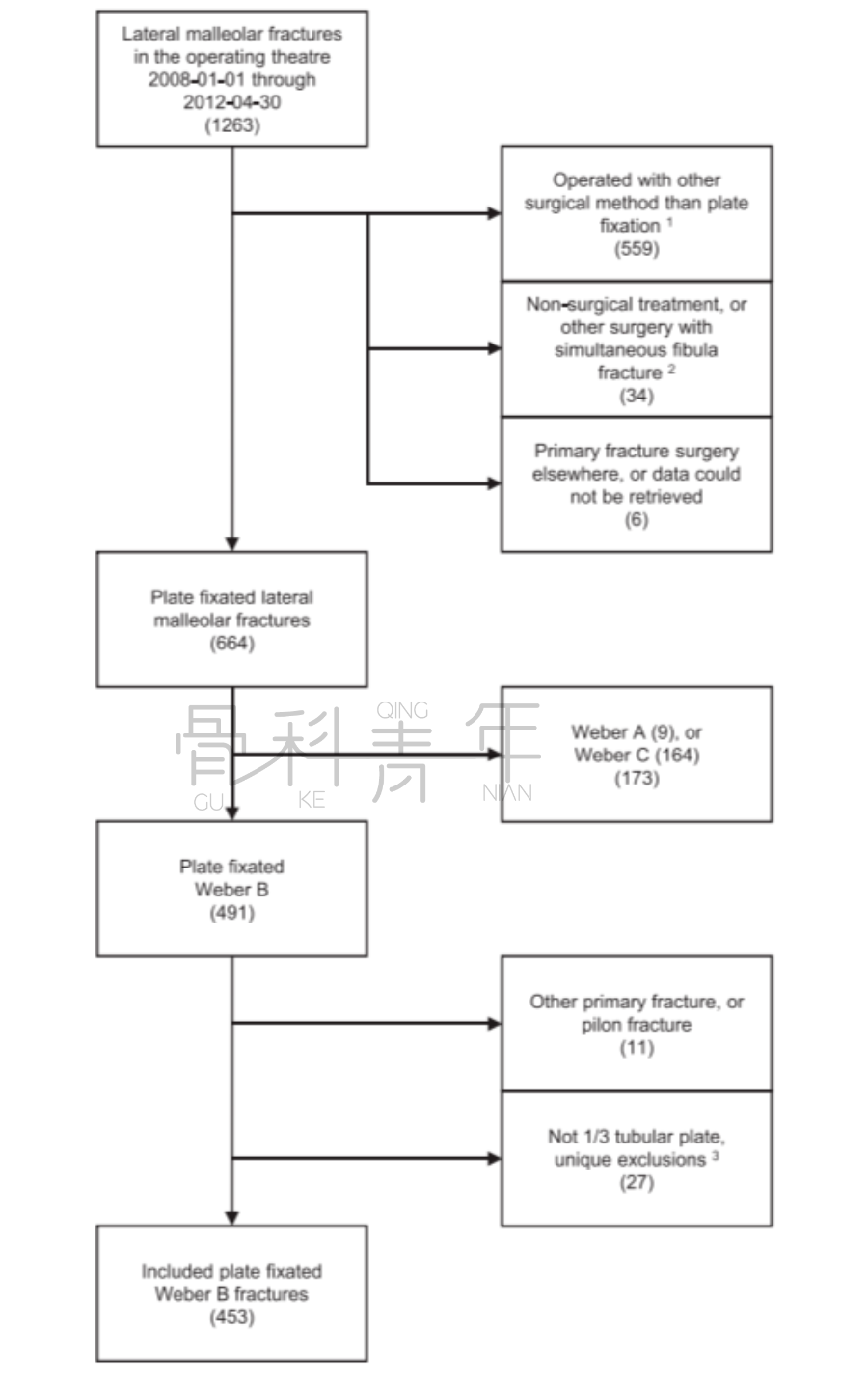
表1 病例纳入流程图。

图1 外侧钢板,作为中和钢板使用,保护拉力螺钉。
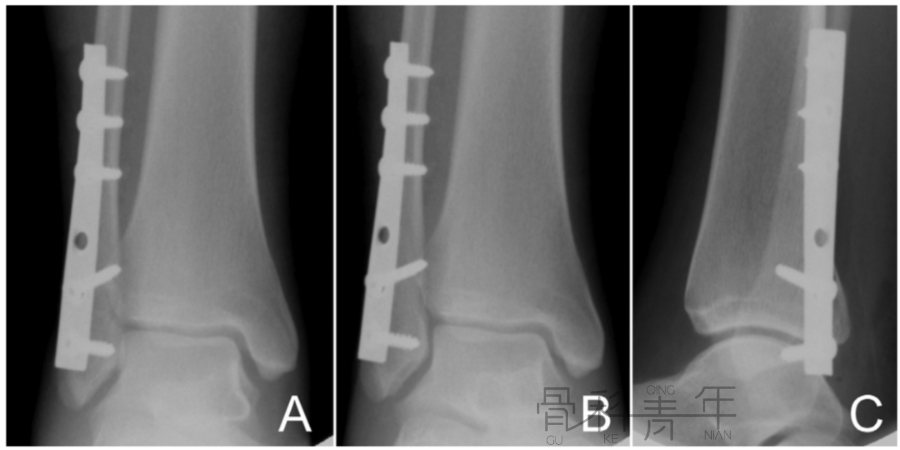
图2 后外侧钢板,作为抗滑钢板使用。
Results(结果)
后外侧钢板术后再手术的风险为13%,而外侧钢板术后为24%;绝对风险降低10%(95% CI:2.5–18),p = 0.02。调整可能的混杂因素后,外侧钢板术后再次手术的比值比为2.2 (95%置信区间:1.17–4.1),p = 0.01。这两种手术方法在并发症发生率方面没有差异:31% vs 34%,p = 0.6,但是外侧钢板固定后的并发症更严重,p = 0.03。钢板定位取决于外科医生的偏好。
[Results: The risk of reoperation was 13% after posterolateral plating, compared with 24% after lateral plating; absolute risk reduction 10% (95% CI: 2.5–18), p = 0.02. After adjusting for possible confounders, the odds ratio of undergoing reoperation after lateral plating was 2.2 (95% CI: 1.17–4.1), p = 0.01. The two surgical methods did not differ with regard to complication frequency: 31% vs 34%, p = 0.6, but complications following lateral plate fixation were more serious, p = 0.03. Plate positioning depended on surgeon preference.]


表3 两组病例并发症比较。
Conclusion(结论)
AO/OTA 44-B骨折外踝后外侧钢板固定可能优于外侧钢板固定,因为计划外二次手术差异较大。
[Conclusion: Posterolateral plate positioning on the lateral malleolus in AO/OTA 44-B-fractures may be preferential to lateral plate positioning, due to a large difference in unplanned secondary surgery.]

本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言












好文章,谢谢分享
70