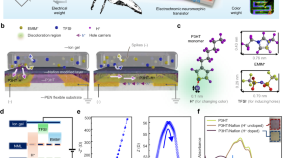
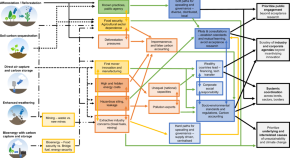
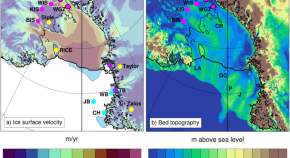
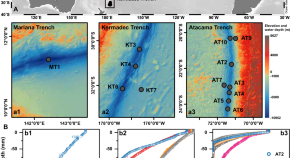
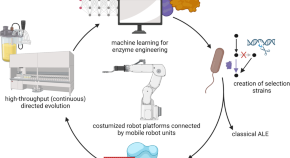
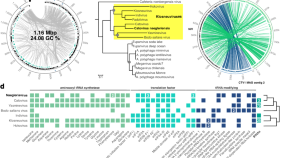
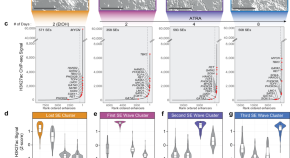
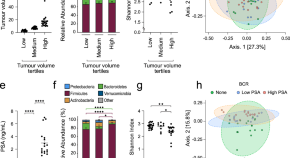
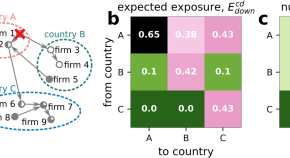
Global-scale magnetosphere convection driven by dayside magnetic reconnection
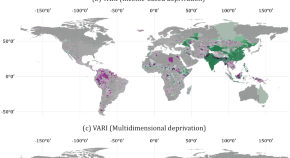
Lei Dai and colleagues study the interaction between solar wind and the planetary magnetosphere. They describe dayside-driven convection patterns, impacting the global magnetic field dynamics.