Cancer Discov:小细胞肺癌对烷基化药物的耐药机制被发现
2022-09-06 MedSci原创 MedSci原创
小细胞肺癌 (SCLC) 约占肺癌的 15%,是一种高度恶性且几乎均致命的疾病。迄今为止,尚无针对 SCLC 的靶向治疗获批,该病仍通常采用常规化疗进行治疗。在过去的几十年中,一线铂类化疗(顺铂或卡铂
小细胞肺癌 (SCLC) 约占肺癌的 15%,是一种高度恶性且几乎均致命的疾病。迄今为止,尚无针对 SCLC 的靶向治疗获批,该病仍通常采用常规化疗进行治疗。在过去的几十年中,一线铂类化疗(顺铂或卡铂联合依托泊苷)取代了先前在 SCLC 中使用的基于烷基化的化疗(环磷酰胺 + 多柔比星 + 长春新碱),因为毒性较低,但疗效不佳。有趣的是,铂类和烷基化化疗的组合可能会提高 SCLC 的无进展生存期。值得注意的是,基于烷基化的化学疗法在初始治疗失败后仍然经常使用,而使用烷基化剂的联合疗法仍在 SCLC 的研究中。此外,尽管这两种方案都不可避免地导致获得性耐药,但研究表明,烷化化疗在对铂类药物耐药的 SCLC 中仍然具有一定的疗效,而反之则不然。无论如何,SCLC 患者的全身治疗在过去几十年中没有显著变化,基于顺铂和烷基化方案的疗效仍然不足,5 年生存率低于 7%。事实上,SCLC 最初对一线治疗很敏感,但大多数患者会因化疗耐药疾病迅速复发,并且由于缺乏替代治疗选择而很少存活超过一年。因此,更好地了解驱动治疗耐药的分子机制具有重要的临床意义,并且对于开发和改进对 SCLC 有效的新疗法是必要的。
在这项新的研究中,圣路易斯华盛顿大学、格勒诺布尔-阿尔卑斯大学和得克萨斯大学的研究人员调查了SCLC细胞如何抵抗化疗造成的损害,以及如何对抗这种损害。这项研究发表在《癌症发现》杂志上。
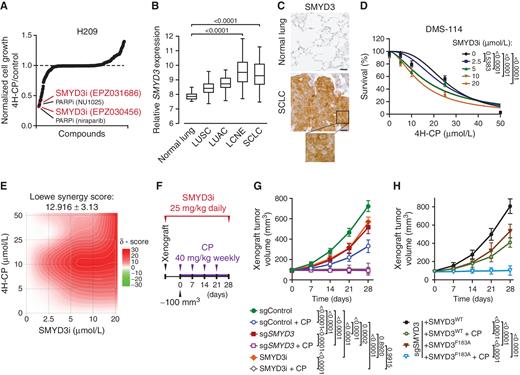
在之前的工作中,科学家们发现一种名为RNF113A的蛋白质与癌细胞修复烷基化损伤的能力有关,烷基化损伤是普通化疗药物的攻击模式。经过仔细检查,研究小组发现RNF113A受另一种蛋白质SMYD3的调节,SMYD3在SCLC细胞和其他癌症中表达量较高。特别是,较高水平的SMYD3与更具侵略性的癌症和更强的抗药性有关。
有了这个新目标,科学家们研究了阻断SMYD3是否能改善化疗药物的效果。
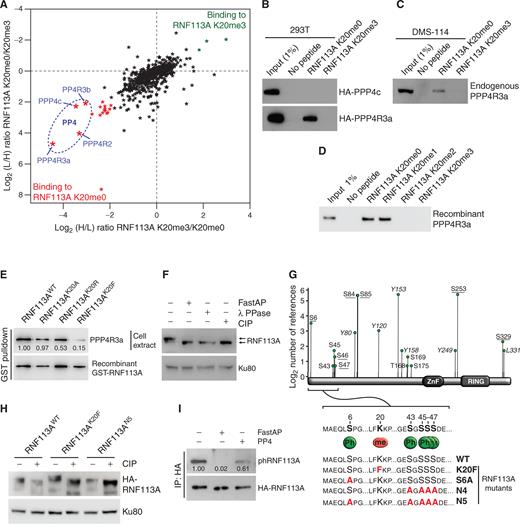
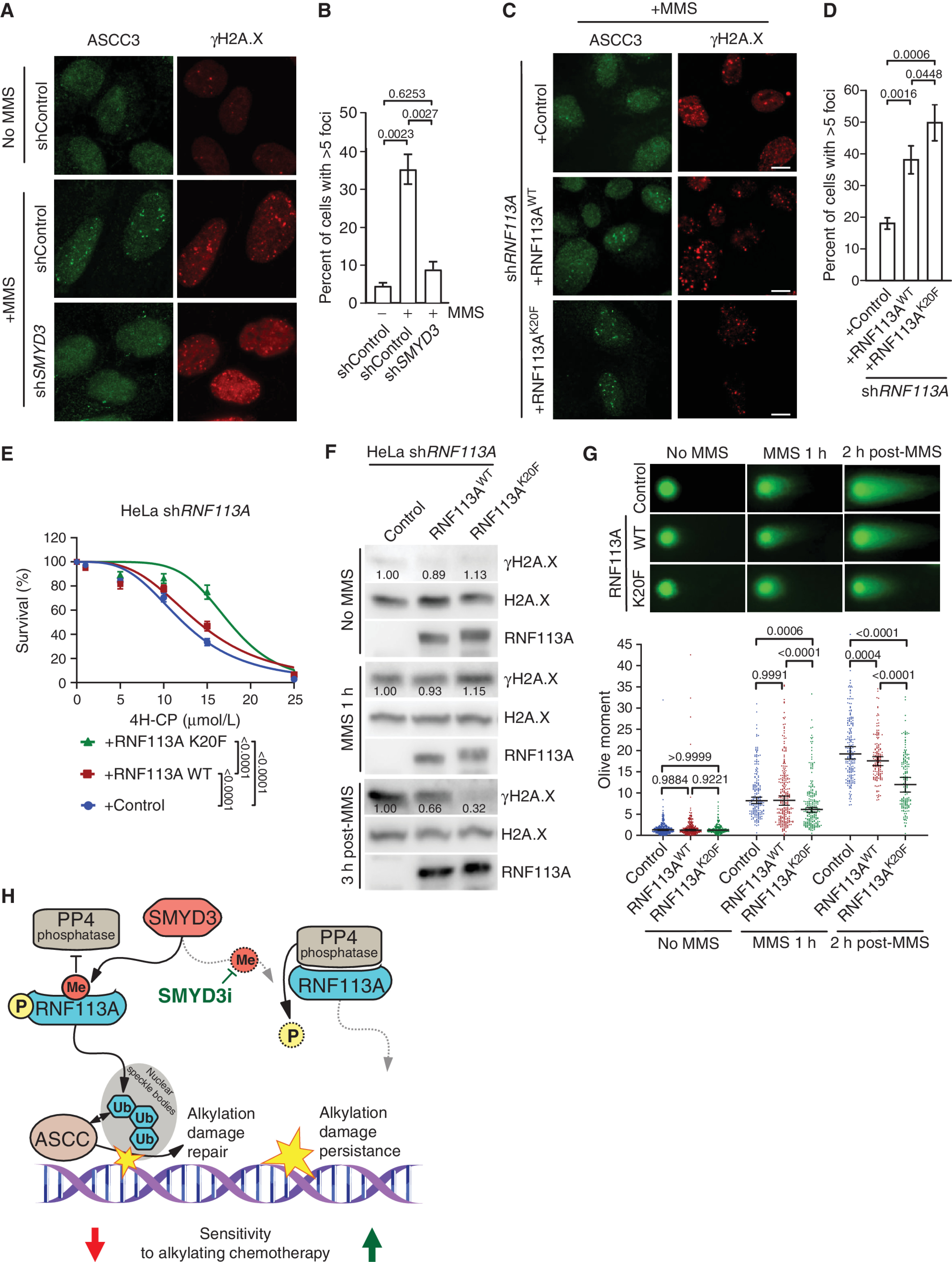
为了研究 SMYD3 在 SCLC 中的影响,研究者将观察范围扩大到患者来源的肿瘤异种移植物和小鼠模型。使用这些模型,发现 SMYD3 的基因缺失或药理学抑制使癌细胞对烷基化治疗剂敏感。为了破译 SMYD3 在 SCLC 中的相关分子机制,研究者进行了生化筛选,将 E3-泛素连接酶 RING 指蛋白 113A (RNF113A) 鉴定为一种新的底物。值得注意的是,RNF113A 最近被描述为对去烷基化修复中激活信号协整复合体 (ASCC) 的功能至关重要 (19, 20)。生化分析表明 RNF113A 活性受烷基化损伤反应的磷酸化调节。我们的蛋白质组学分析表明,SMYD3 介导的 RNF113A 甲基化阻止了磷酸酶 PP4 的结合,维持 RNF113A 的活性以维持其在烷基化损伤反应中的作用。最后,我们观察到具有活性 SMYD3-RNF113A 信号传导的细胞对 DNA 烷基化损伤的抵抗力更强。因此,这项工作通过促进由 RNF113A E3 连接酶活性升高诱导的脱烷基化修复途径,揭示了 SCLC 中细胞对基于烷基化的化学疗法的耐受的新机制。研究者提出了将 SMYD3 靶向作为克服 SCLC 耐药性发展的新策略的基本原理。
由于环磷酰胺与基于铂类化疗药物相比具有更强的副作用,近几十年来,环磷酰胺在某种程度上已不再受到青睐,但新的研究可能意味着它值得被重新提起。该团队希望这项研究能够为一种侵略性的癌症带来新的治疗方法,目前对这种癌症的选择很少。
有趣的是,我们发现 SMYD3 和 RNF113A 在最近表征的四种 SCLC 亚型之间都有相似的表达。 因此,靶向该途径可能适用于所有 SCLC 亚型,并且所描述的途径很可能参与观察到 SMYD3 过表达的其他肿瘤环境。 由于癌症发展为抵抗抗肿瘤治疗的多种逃逸途径,通常需要将细胞毒性化学疗法与一种或多种靶向疗法相结合。 这里确定的新机制为 SMYD3 抑制剂的治疗用途提供了基本原理,以减轻烷基化化疗在 SCLC 患者一线或二线治疗中的疗效。
该研究的共同第一作者Nima Mosammaparast说:“我们正在与其他一些团体讨论尽快开始一期临床试验。小细胞肺癌患者迫切需要更好的治疗方法,我对这里的可能性感到非常兴奋。”
原始出处:
Lukinović V, Hausmann S, Roth GS, Oyeniran C, Ahmad T, Tsao N, Brickner JR, Casanova AG, Chuffart F, Benitez AM, Vayr J, Rodell R, Tardif M, Jansen PWTC, Couté Y, Vermeulen M, Hainaut P, Mazur PK, Mosammaparast N, Reynoird N.SMYD3 Impedes Small Cell Lung Cancer Sensitivity to Alkylation Damage through RNF113A Methylation-Phosphorylation Cross-talk.Cancer Discov. 2022 Sep 2;12(9):2158-2179. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0205.PMID: 35819319
PDF文件下载:点击打开
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言







#耐药机制#
56
#Dis#
35
#ISC#
65
#小细胞肺癌#这项研究值得后续进行药物开发,包括针对E3泛素化的降解的#PROTAC#类药物开发,以及针对#SMYD3# 和 RNF113A#靶点#的药物开发,可能都具有一定的潜力。
144