【衡道丨干货】WHO图注英文学习手帐 (生殖细胞肿瘤-无性细胞瘤与卵黄囊瘤)
2023-11-23 衡道病理 衡道病理 发表于上海
无性细胞瘤是一种原始生殖细胞肿瘤,由无特异性分化的细胞组成。
衡道病理特邀撰稿作者翻译了WHO部分图⽚的图注,并用手帐的⽅式进行中英对照,且通过不同颜色的划线将晦涩难懂的英文单词与中⽂翻译同时标注,希望对专业英文的学习有所帮助。上一期分享了生殖细胞肿瘤中的成熟型畸胎瘤与未成熟型畸胎瘤,本期将带来生殖细胞肿瘤中的无性细胞瘤与卵黄囊瘤。由于本篇目的以英文学习为主,篇幅有限,故未对各个疾病进行详细阐述。全部图片均来自WHO,若有不恰当之处,还请评论区指正。
WHO图注英文学习手帐
一、Dysgerminoma
无性细胞瘤
Definition
Dysgerminoma is a primitive germ cell tumour composed of cells showing no specific differentiation.
定义
无性细胞瘤是一种原始生殖细胞肿瘤,由无特异性分化的细胞组成。
ICD-O coding
9060/3 Dysgerminoma
ICD-O编码
9060/3 无性细胞瘤
Histopathology
Sheets and nests of monotonous tumour cells are separated by thin fibrous septa containing lymphocytes. Less common patterns include cords, trabeculae, solid tubules, and pseudoglands. Tumour cells are polygonal, with well-defined cell borders, abundant clear or eosinophilic cytoplasm, and one central nucleus with one or two prominent nucleoli. Nuclear contours may have an angular, squared-off appearance. Mitoses are common. Scattered syncytiotrophoblastic cells are present in a minority of tumours. The surrounding stroma may contain poorly formed granulomas, which may obscure the tumour, especially in metastatic sites. Rarely, dysgerminoma may contain foci of spermatocytic tumour-like cells.
组织病理学
单一的肿瘤细胞呈片状、巢状,被含有淋巴细胞的纤细的纤维间隔分开。较不常见的类型包括索状、小梁状、实性小管和假腺体。肿瘤细胞呈多边形,细胞边界清晰,胞质丰富,透明、嗜酸性,有一个或两个突出核仁位于中央。核轮廓可呈棱角或方形外观,核分裂很常见。少数肿瘤中散在的合胞体滋养层细胞。周围间质可能含有形成不良的肉芽肿,这可能掩盖肿瘤,特别是在转移部位。罕见情况下,无性细胞瘤可能含有精原细胞瘤样细胞灶。
Immunohistochemically
Dysgerminoma is immunohistochemically positive for SALL4, OCT4, LIN28, NANOG, KIT (CD117), and D2-40. Cytokeratins may be focally positive. EMA, CD30, and glypican-3 (GPC3) are negative.
免疫组化
无性细胞瘤免疫组化SALL4、OCT4、LIN28、NANOG、KIT (CD117)和D2-40呈阳性。CK可能局部呈阳性。EMA、CD30和glypican-3 (GPC3)均为阴性。
Essential and desirable diagnostic criteria
Essential: uniform rounded primitive germ cells with clear cytoplasm and macronucleoli, arranged in nests or cords separated by thin fibrous septa containing lymphocytes.
Desirable: immunohistochemical confirmation by positive staining for OCT4 or SALL4, KIT (CD117), and/or D2-40.
必需和理想的诊断标准
必需:均一的圆形原始生殖细胞,有透明胞质和大核仁,排列呈巢状或条索状,被含有淋巴细胞的纤细纤维分隔。
理想:免疫组化染色表示OCT4或SALL4, KIT (CD117)和/或D2-40阳性。
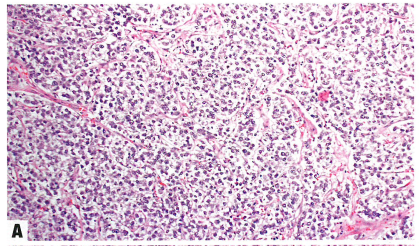
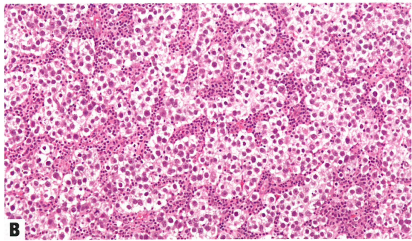
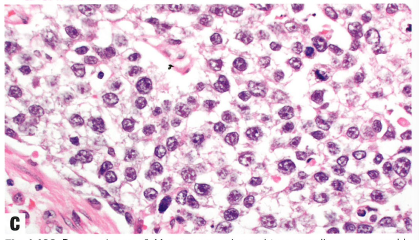
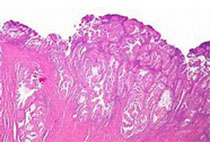
Fig.1.106 Dysgerminoma.
A Monotonous polygonal tumour cells are arranged in nests defined by thin fibrous septa.
B Fibrous septa between aggregates of tumour cells contain variable numbers of lymphocytes.
C The nuclei of dysgerminoma tumour cells often exhibit angular or squared-off contours and prominent nucleoli. Mitoses are common.
图1.106无性细胞瘤。
A 单一的多边形肿瘤细胞排列呈巢状,被纤细的纤维分隔。
B 肿瘤细胞巢之间的纤维间隔含有不同数量的淋巴细胞。
C 无性细胞瘤的细胞核常有成角或呈立方形,核仁突出。核分裂常见。
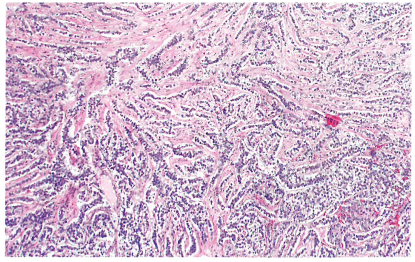
Fig. 1.107 Dysgerminoma. The tumour cells grow in a corded and trabecular pattern.
图1.107无性细胞瘤。肿瘤细胞呈条索状和小梁状生长。
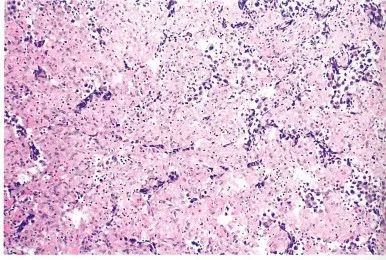
Fig.1.108 Dysgerminoma. Granulomatous inflammation (epithelioid histiocyte lymphocytes) in the fibrous septa of dysgerminoma may be extensive in some obscuring the tumour cells.
图.1.108无性细胞瘤。在无性细胞瘤中,纤维分隔中的肉芽肿性炎(上皮样组织细胞、淋巴细胞)可能广泛地掩盖肿瘤细胞。
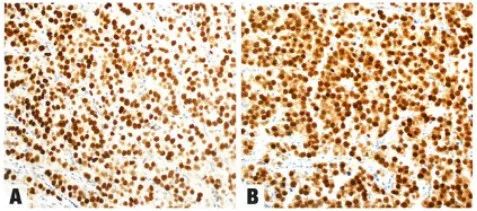
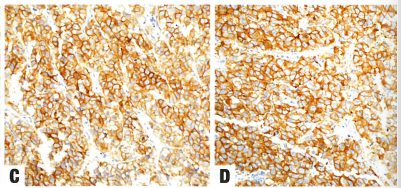
Fig.1.109 Dysgerminoma exhibits nuclear staining for SALL4 (A) and OCT4 (B) and membranous staining for KIT (CD117) (C) and D2-40 (D).
图1.109无性细胞瘤显示SALL4 (A)和OCT4 (B)的核染色,KIT (CD117) (C)和D2-40 (D)的膜染色。
二、Yolk sac tumour
卵黄囊瘤
Definition
Yolk sac tumour (YST) is a primitive germ cell tumour displaying multiple patterns reflecting endodermal extraembryonal differentiation (secondary yolk sac and allantois) or, less commonly, endodermal somatic tissues (intestine, liver, and mesenchyme).
定义
卵黄囊肿瘤(YST)是一种原始生殖细胞肿瘤,表现出多种模式,反映了内胚层胚胎外分化(第二卵黄囊和尿囊),或者少见内胚层体细胞组织(肠、肝和间质)。
ICD-O coding
9071/3 Yolk sac tumour NOS
ICD-O编码
9071/3 卵黄囊肿瘤 NOS
Histopathology
Multiple patterns are usually present, most commonly a reticular/ microcystic pattern (a meshwork of anastomosing spaces and cysts lined by a single layer of tumour cells). Other patterns include the endodermal sinus pattern (a proliferation of Schiller-Duval bodies, which are round or elongated tumour cell-lined papillae with a large central vessel, protruding into a cystic space surrounded by tumour cells), papillary pattern, solid pattern, festoon pattern (complex ribbons and undulating cords), and glandular pattern (endometrioid-like or intestinal-type). Less common patterns are the polyvesicular-vitelline pattern (numerous vesicles and cysts within cellular stroma), parietal pattern (tumour cells embedded in linear bands of basement membrane material), mesenchyme-like pattern (tumour cells scattered in oedematous or myxomatous connective tissue), and hepatoid pattern).
组织病理学
通常存在多种模式,最常见的是网状/微囊状(吻合的网状和被覆单层排列肿瘤细胞的囊肿)。其他类型包括内胚窦模式(Schiller-Duval小体增生,呈圆形或细长的肿瘤细胞排列呈乳头状状,中央有一个大的血管轴心,突出到被肿瘤细胞包围的囊腔中),乳头状,实体型,花环样(复杂的带状和波纹条索状)和腺样(子宫内膜样或肠型)。较不常见的是多囊-卵黄囊模式(细胞间质内有大量的囊泡和囊肿)、壁型(肿瘤细胞嵌在基底膜样物质中)、间质样型(肿瘤细胞分散在水肿或黏液性结缔组织中)和肝样型。
Tumour cell appearance depends on the growth pattern, but the cells usually exhibit variable atypia, clear cytoplasm, and hyaline globules. In older women with a coexisting ovarian or endometrial carcinoma, YST typically exhibits a reticular pattern.
肿瘤细胞的外观取决于生长模式,但细胞通常表现为不同程度的异型性,胞质透明,还有透明小球。在同时患有卵巢或子宫内膜癌的老年妇女中,YST通常呈网状结构。
Immunohistochemical
Positive immunohistochemical markers include SALL4, LIN2, AFP (often focal and weak), glypican-3 (GPC3), and ZBTB16, as well as CDX2 in the intestinal-type pattern, Hep Par-1 in the hepatoid pattern, and TTF1 in the foregut/respiratory pattern.
免疫组化
阳性免疫组织化学标志物,包括SALL、LIN28、AFP(通常是局灶性和弱阳)、glypicn -3 (GPC3)和ZBTB16,以及肠型CDX2阳性、肝样型Hep Par-1阳性和前肠/呼吸型TTF1阳性。
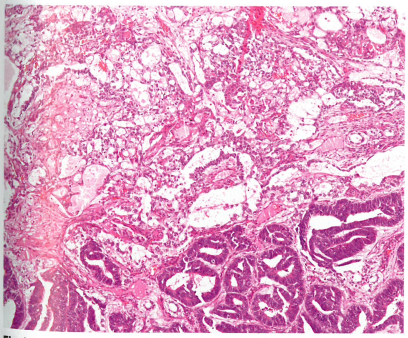
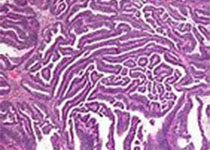
Fig. 1.110 Yolk sac tumour. Yolk sac tumour typically exhibits multiple patterns: reticular/microcystic pattern (top), endodermal sinus pattern (centre), and endometrioid-like glandular pattern (bottom).
图1.110卵黄囊瘤。卵黄囊瘤典型表现为多种形态:网状/微囊型(上),内胚窦型(中),子宫内膜样型(底部)。
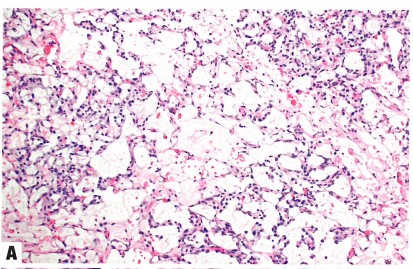
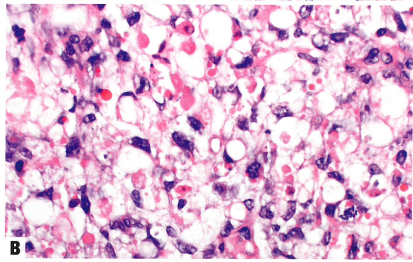
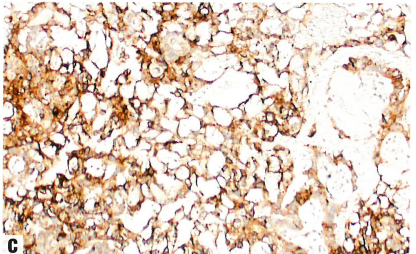
Fig.1.111 Yolk sac tumour.
A The reticular/microcystic pattern consists of interanastomosing spaces and cysts lined by tumour cells.
B Eosinophilic hyaline globules are common in yolk sac tumour, although not specific for this tumour type.
C Glypican-3 (GPC3) immunohistochemistry.
图1.111卵黄囊瘤。
A 网状/微囊型由相互吻合的间隙和衬覆肿瘤细胞的囊肿组成。
B 嗜酸性透明小球在卵黄囊肿瘤中很常见,尽管对这种肿瘤类型没有特异性。
C Glypican-3 (GPC3)免疫组化阳性。
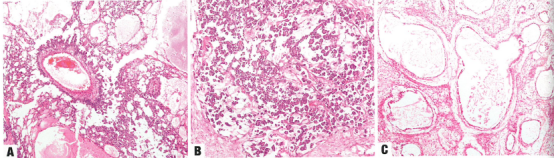
Fig. 1.112 Yolk sac tumour.
A The Schiller-Duval body is a tumour cell-lined papilla with a large central vessel, occupying a cystic space within endodermal sinus-pattern yolk sac tumour.
B Papillary pattern.
C The polyvesicular vitelline pattern of yolk sac tumour is a honeycomb-like pattern of numerous variably sized vesicles and cysts within fibrous stroma.
图1.112卵黄囊瘤。
A Schiller-Duval小体是一种由肿瘤细胞排列的乳头状结构,中央有一个大的血管,出现在内胚窦型卵黄囊瘤内的囊性间隙中。
B 乳头状型。
C 卵黄囊瘤的多囊卵黄囊模式是纤维间质内存在许多大小不等的囊泡和囊肿,形成蜂窝状结构。
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言










#生殖细胞肿瘤# #卵黄囊瘤# #无性细胞瘤# #原始生殖细胞肿瘤#
32