Nature—诺奖级别的工作:日本科学家揭示LKB1-SIK3-HDAC4信号通路是调控NREM睡眠的关键机制
2022-12-11 神经科学临床和基础 神经科学临床和基础 发表于上海
这些发现表明,NREM睡眠的数量和深度由不同的兴奋性神经元群通过共同的细胞内信号调节。
中文摘要
科学家在阐明神经环路水平的睡眠和觉醒调控机制方面取得了进展。然而,调节睡眠的细胞内信号通路以及采用这些细胞内机制调控睡眠的神经元集群在很大程度上仍然未知。在这里,科学家使用小鼠的正向遗传学方法,将组蛋白去乙酰化酶4(HDAC4)鉴定为睡眠调节分子。Hdac4(一种盐诱导激酶3(SIK3)3的底物)的单倍剂量不足增加了睡眠。相比之下,在神经元中剔除SIK3或其上游激酶LKB1的小鼠,或具有对SIK3磷酸化产生抗性的Hdac4S245A突变的小鼠表现出睡眠下降。这些发现表明LKB1-SIK3-HDAC4构成了调节睡眠和觉醒的信号级联。他们还对特定神经元和大脑区域的SIK3和HDAC4进行了靶向操纵,发现位于大脑皮层和下丘脑的兴奋性神经元中的SIK3信号分别正向调节非快速眼动睡眠(NREMS)EEGδ功率和NREMS睡眠量。通过增强Sik3功能或睡眠剥夺可在皮层谷氨酸能神经元中调节突触功能相关的转录过程。这些发现表明,NREM睡眠的数量和深度由不同的兴奋性神经元群通过共同的细胞内信号调节。这项研究为连接细胞内事件和控制NREM的神经环路水平机制奠定了基础。
英文摘要
Progress has been made in the elucidation of sleep and wakefulness regulation at the neurocircuit level. However, the intracellular signalling pathways that regulate sleep and the neuron groups in which these intracellular mechanisms work remain largely unknown. Here, using a forward genetics approach in mice, we identify histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) as a sleep-regulating molecule. Haploinsufficiency of Hdac4, a substrate of salt-inducible kinase 3 (SIK3), increased sleep. By contrast, mice that lacked SIK3 or its upstream kinase LKB1 in neurons or with a Hdac4S245A mutation that confers resistance to phosphorylation by SIK3 showed decreased sleep. These findings indicate that LKB1-SIK3-HDAC4 constitute a signalling cascade that regulates sleep and wakefulness. We also performed targeted manipulation of SIK3 and HDAC4 in specific neurons and brain regions. This showed that SIK3 signalling in excitatory neurons located in the cerebral cortex and the hypothalamus positively regulates EEG delta power during non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREMS) and NREMS amount, respectively. A subset of transcripts biased towards synaptic functions was commonly regulated in cortical glutamatergic neurons through the expression of a gain-of-function allele of Sik3 and through sleep deprivation. These findings suggest that NREMS quantity and depth are regulated by distinct groups of excitatory neurons through common intracellular signals. This study provides a basis for linking intracellular events and circuit-level mechanisms that control NREMS.



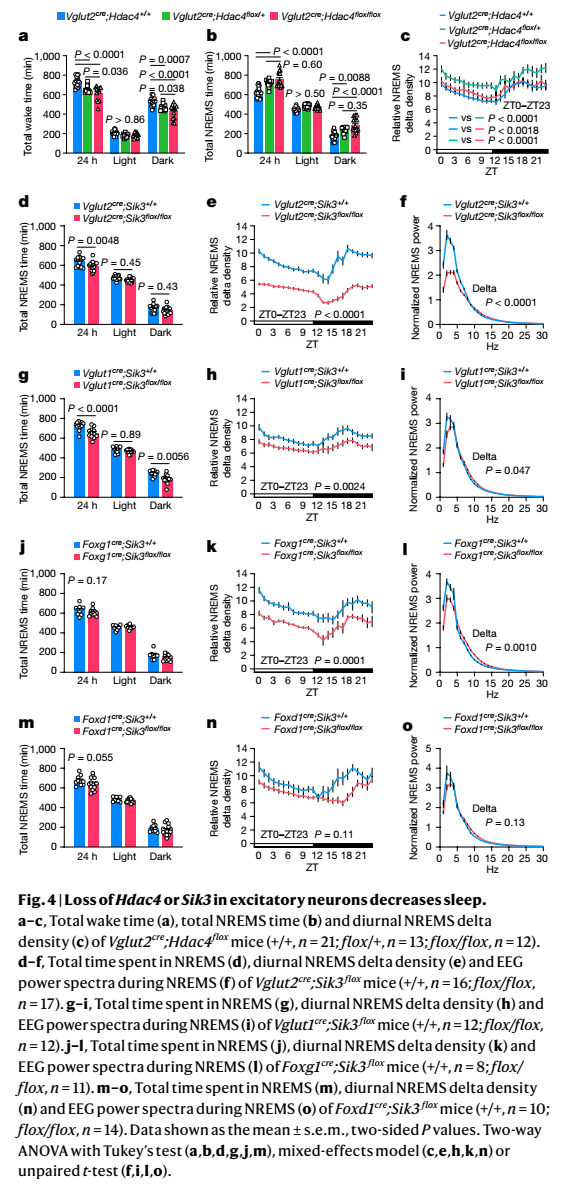

参考文献:Kinase signalling in excitatory neurons regulates sleep quantity and depth.Nature. 2022 Dec 7. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05450-1.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言








签到学习
51